
Hydrophilic sugar phosphate backbone professional#
Professional Capstone Project (PSY-495).Professional Application in Service Learning I (LDR-461).Expanding Family and Community (Nurs 306).Critical Thinking In Everyday Life (HUM 115).Essentials for advanced professional nurse and professional roles (D025).Concepts of Medical Surgical Nursing (NUR 170).Financial Statement Analysis/Business Valuation (ACC345).Nursing B43 Nursing Care of the Medical Surgical (NURS B43).Alterations in Adult Health 1 (NSG 311).Perspectives in the Humanities (HUM 100).Global Infectious Diseases and Social Justice: Lessons from Science, History, & Humanities (SCILIVSY 26).Introduction to Biology w/Laboratory: Organismal & Evolutionary Biology (BIOL 2200).Medical-Surgical Nursing Clinical Lab (NUR1211L).Foundational Literacy Skills and Phonics (ELM-305).Kilpatrick S.T 2011 Lewin's Genes X, 10th Edition, Jones and Bartlett Publishers: London These two sugars only differ by one -OH group being changed to an -H, but provides different capabilities for each molecule. On on the other hand, the sugar in the backbone of RNA is called ribose.
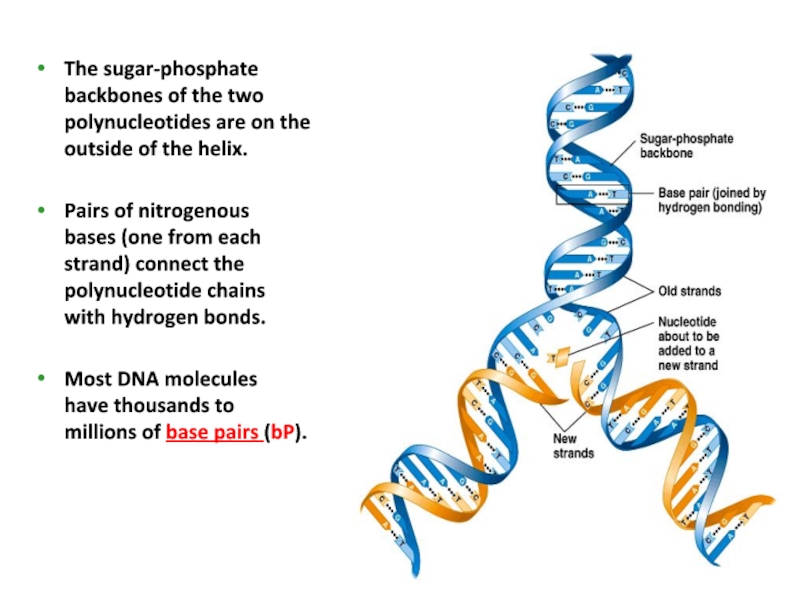
In DNA, the sugar involved is deoxyribose. However, their sugar phosphate backbone differs slightly. RNA and DNA are both examples of phosphodiesters and have a very similar structure. One turn of this helix is 34nm long, the diameter of it is 2nm, and there are ten bases attached per turn at 0.34nm. These features make DNA can repel water and would not hydrolysed and breakdown by the aqueous environment. DNA is very stable due to rungs of “ladder” is hydrophobic and phosphate sugar backbone of DNA is negatively charged. The purpose of this twisting is to protect the bases inside it, and prevent them from being damaged by the environment. one runs 3' to 5', the other run 5' to 3'. This is done by the sugar phosphate backbone twisting around itself in a coil. Figure 1 Diagram showing the sugar phosphate backbone of DNA, and the nitrogenous bases attached to it, forming a nucleotide Structure of DNAĭNA is wound into an right-handed double helix.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
